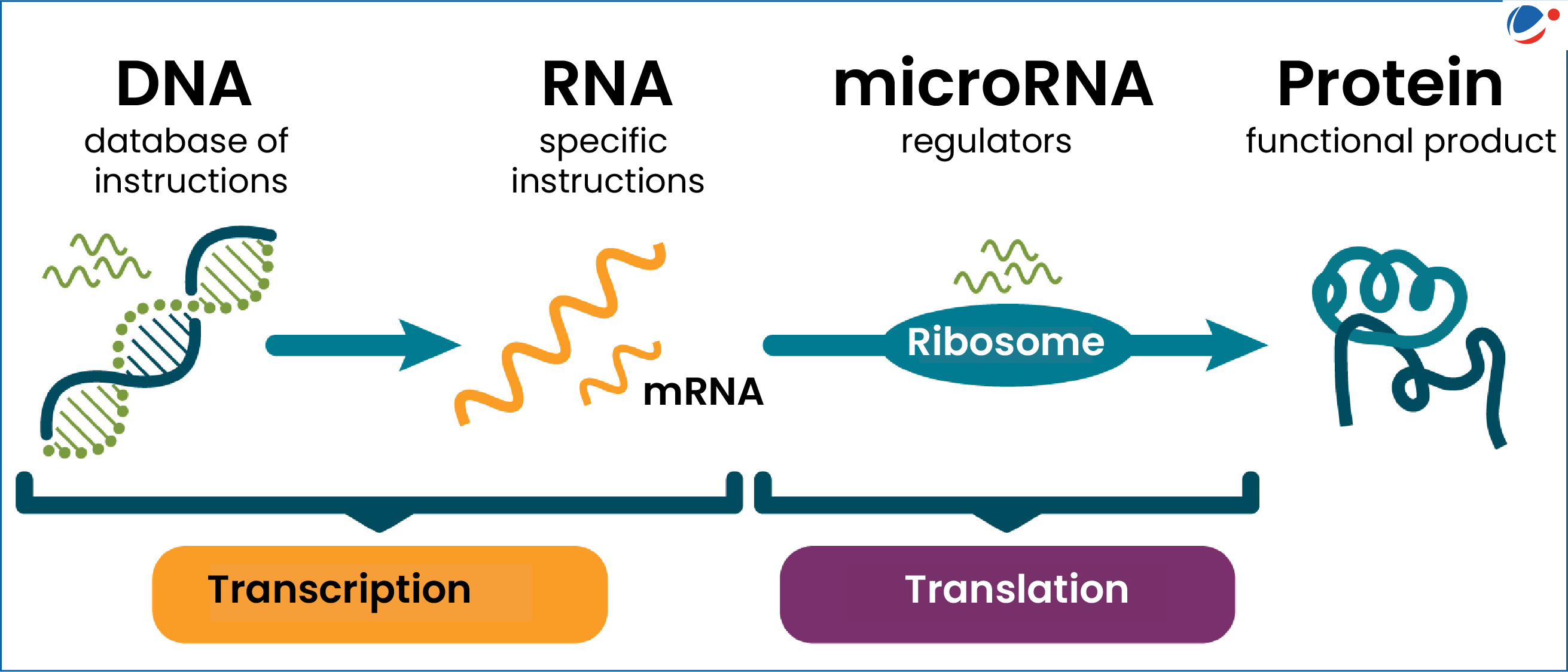
The discovery of microRNA has revolutionized our understanding of gene regulation, establishing it as a pivotal area in molecular biology. Initially unearthed by Nobel laureate Gary Ruvkun during his research on the C. elegans roundworm, microRNA has since been recognized for its crucial role in various physiological processes. In 2024, Ruvkun and his colleague Victor Ambros received the Nobel Prize for their groundbreaking work, which has opened new avenues for RNA therapies in treating numerous diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s. Despite skepticism from the evolutionary biology community in the early stages, the significance of microRNA in regulating gene expression has been ultimately validated, showcasing its impact across species, including humans. As research continues to evolve, microRNA therapies are currently in clinical trials, marking a significant leap toward innovative medical solutions.
The unveiling of small non-coding RNAs, known as microRNAs, has been a cornerstone in advancing our grasp of genetic control mechanisms. This tiny RNA segment, first identified by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in the early 1990s, has sparked immense interest in biomedical research, particularly concerning treatments for chronic diseases. These key regulators of gene expression are being intensely studied for their therapeutic potential, with ongoing clinical trials targeting a range of conditions from neurodegenerative illnesses to cancer. What began as a niche discovery within the C. elegans model organism has swiftly transformed into a fundamental concept influencing various scientific domains, illustrating how tiny molecules can wield significant biological power. Overall, the trajectory from microRNA discovery to its modern applications embodies the dynamic interplay between basic research and clinical advancement.
The Groundbreaking Discovery of MicroRNA
In 1992, the field of genetic research experienced a significant breakthrough with the discovery of microRNA by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros. Initially, their work went unnoticed by many in the evolutionary biology community, who were skeptical about the relevance of microRNAs beyond the C. elegans model organism. However, this discovery marked a pivotal moment in gene regulation, highlighting how tiny RNA molecules could play a crucial role in the control of gene expression. As Ruvkun and Ambros shared their findings in the renowned journal Cell, the implications of their research began to unfold, showcasing a new layer of complexity in the biological processes of organisms.
Fast forward to today, and microRNA has become a cornerstone of molecular biology, altering our understanding of gene regulation across various species, including humans. Research has revealed that approximately 1,000 microRNAs are encoded in the human genome, indicating their vital role in regulating most protein-coding genes. This profound implication for biology and medicine has not only sparked increased interest in RNA research but has also ushered in the development of innovative RNA therapies aimed at treating a plethora of diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are microRNAs and how did Gary Ruvkun contribute to their discovery?
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNAs that play a critical role in gene regulation. Gary Ruvkun, along with Victor Ambros, discovered miRNAs in 1992 while studying the C. elegans roundworm. Their groundbreaking research revealed a new level of gene regulation, which later earned them the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
How do microRNAs affect gene regulation in humans?
MicroRNAs are essential for regulating gene expression in humans, affecting over 1,000 genes involved in the protein production process. Ruvkun’s research on miRNAs has shown their conservation across species and their fundamental role in cellular functions, highlighted by their involvement in various diseases like cancer and heart disease.
What implications does microRNA research have for RNA therapies?
Research in microRNAs has vast implications for RNA therapies targeting diseases such as Alzheimer’s, cancer, and Crohn’s Disease. These therapies are currently undergoing clinical trials, leveraging the regulatory capabilities of miRNAs to develop innovative treatments that can improve patient outcomes.
What accolades did Gary Ruvkun receive for his work on microRNA discovery?
For their pioneering discovery of microRNAs and contributions to understanding gene regulation, Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros were awarded the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, recognizing their significant impact on molecular biology and genetics.
How do microRNAs contribute to the understanding of diseases?
MicroRNAs significantly contribute to our understanding of various diseases by regulating genes involved in critical biological pathways. Ruvkun’s research has shown that alterations in miRNA expression can lead to disease pathogenesis, providing targets for new therapeutic interventions in conditions like cancer, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
What future prospects exist for microRNA research and therapies?
The future prospects for microRNA research are promising, with ongoing studies focusing on their role in gene regulation and potential therapeutic applications. As understanding deepens, we expect advancements in RNA therapies that could transform treatment paradigms for multiple diseases, driven by foundational research like that of Gary Ruvkun.
What role did federal funding play in the advancement of microRNA research?
Federal funding has been pivotal in advancing microRNA research. Gary Ruvkun’s work was largely supported by the National Institutes of Health, underscoring the importance of government investment in scientific research, which has led to significant breakthroughs in understanding gene regulation and the development of new RNA-based therapies.
How did the scientific community initially respond to the discovery of microRNAs?
Initially, the scientific community showed limited interest in the discovery of microRNAs, as many believed the findings were specific to C. elegans and not applicable to other species. However, as research progressed, the significance of microRNAs in gene regulation and their presence in various organisms, including humans, became widely recognized, leading to increased interest and research funding.
In what ways can microRNA discovery lead to technological advancements in medicine?
MicroRNA discovery can lead to significant technological advancements in medicine by facilitating new diagnostic tools and therapies that target gene expression. Innovations driven by miRNA research can enhance precision medicine approaches, allowing for more effective treatments tailored to individual genetic profiles.
What challenges and opportunities exist in the field of microRNA research today?
The field of microRNA research today faces challenges such as funding cuts and the need for more robust models for studying their functions. However, significant opportunities exist in the form of developing novel RNA-based therapies and expanding our understanding of their roles in various biological processes and diseases.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros discovered microRNA in 1992, leading to a 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
| Their discovery introduced a new level of gene regulation in the C. elegans roundworm. |
| Initial interest was low, with recognition coming mostly from NIH-funded RNA researchers and the ‘worm community.’ |
| MicroRNAs are now known to play critical roles in development, function, and disease treatment, with therapies for conditions like cancer and Alzheimer’s in clinical trials. |
| Ruvkun emphasizes the importance of federal funding in driving scientific breakthroughs and supporting research. |
| He raises concerns about potential cuts to funding and its implications for the future of scientific research in the U.S. |
| Ruvkun’s research contributed to the growth of pharmaceutical companies focused on RNA therapeutics, highlighting the economic impact of basic research. |
Summary
MicroRNA discovery has fundamentally reshaped our understanding of gene regulation and its implications in various diseases. Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros’s groundbreaking work paved the way for innovative therapies in heart disease, cancer, and more. While the initial reception was tepid, the significant advancements in RNA research have now established microRNAs as crucial components in the field of genetics. Continued support for scientific research is vital, not only for the advancement of medical therapies but also for maintaining the United States’ position as a leader in scientific innovation.